Explore More
Bio Gas
Biogas can be produced by fermenting organic material in absence of air or
oxygen with the help of bacteria to break down materials to intermediate stage such
as alcohol and fatty acids and finally to methane, carbon dioxide and water this
process is called anaerobic fermentation.
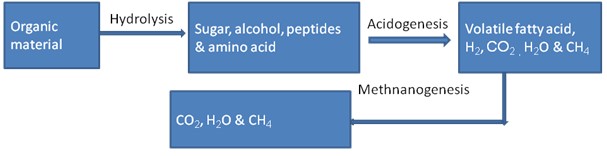
Phase 1: Hydrolysis
The waste materials of plant and animal origins consist mainly of
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and inorganic materials. Large molecular complex
substances are solubilized into simpler ones with the help of extracellular enzyme
released by the hydrolysis bacteria. This stage is also known as polymer breakdown
stage. For example, the cellulose consisting of polymerized glucose is broken down
to dimeric, and then to monomeric sugar molecules (glucose) by cellulolytic bacteria.
Phase 2: Acidification
The sugar molecules produced in phase 1 is fermented under anaerobic
condition into various acids with the help of enzymes produced by the acid forming
bacteria. At this stage, the acid-forming bacteria break down molecules of six atoms
of carbon (glucose) into molecules of lesser atoms of carbon (acids) which are in a
more reduced state than glucose. The principal acids produced in this process are
acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid and ethanol.
Phase 2: Methanization
The acids produced in phase 2 are further processed by methanogenic
bacteria in to methane. The reactions that takes place in the process of methane
production is called Methanization.
